Hearing Loss VA Ratings and Service Connection
By Telemedica
11/21/2025
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Hearing Loss in Veterans
- How the VA Rates Hearing Loss
- How the VA Evaluates Hearing Loss
- How Hearing Loss Tests are Calculated
- Proving Service Connection for Hearing Loss
- VA Disability Rating for Bilateral Hearing Loss
- VA Ratings for Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
- VA Hearing Disability Rates 2026
- How to File a VA Claim for Hearing Loss
- Medical Evidence Wins Claims
- Final Thoughts
- (FAQs) Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the VA rating for hearing loss?
- What is the maximum VA rating for hearing loss?
- Is hearing loss a VA presumptive condition?
- Are there any VA secondary conditions to hearing loss?
- Is it hard to get VA disability for hearing loss?
- Can you get disability for hearing loss and tinnitus?
- What is the VA rating for hearing loss with hearing aids?
- How much hearing loss does it take to qualify for disability?
For many veterans, years of exposure to gunfire, aircraft, explosions, and heavy machinery lead to long-term hearing problems that affect daily communication and quality of life.
Knowing how the VA evaluates hearing loss can make the difference between a low rating and the compensation you rightfully deserve.
This veteran’s guide explains how you can get a VA rating for hearing loss, including how the VA tests your hearing, calculates ratings, and what evidence you need to qualify.
Key Takeaways
- The VA rates hearing loss at 0%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, or 100%, depending on the severity of your condition.
- The VA relies on two specific tests to evaluate hearing loss: the Pure Tone Threshold Average (PTA) and the Maryland CNC test, which measures the percent of speech discrimination.
- All VA hearing tests must be performed by a state-licensed audiologist and conducted without hearing aids, since the VA measures your natural hearing ability.
Hearing Loss in Veterans

Hearing loss is one of the most common VA disability claims, with over 1.5 million veterans receiving compensation as of FY 2024. Among Veterans with audiograms, a subset experience severe bilateral hearing loss.
Years of exposure to loud noises in military settings, such as gunfire, explosions, aircraft, and heavy machinery, make service members particularly susceptible to the effects of noise-induced hearing loss.
VA audiology services offer comprehensive hearing care tailored to your needs, designed to improve communication, enhance safety, and enhance the quality of life, while reducing risks such as social isolation, depression, and cognitive decline.
How the VA Rates Hearing Loss
The VA rates hearing loss under CFR Title 38, Part 4, Schedule for Rating Disabilities, Diagnostic Code (DC) 6100, with possible VA ratings of 0%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, or 100%.
How the VA Evaluates Hearing Loss
A state-licensed audiologist must do a hearing exam for VA disability purposes.
The exam includes two main tests:
- The Maryland CNC Test: Measures how well you understand spoken words (speech discrimination).
- The Pure Tone Audiometry Test: Measures how softly you can hear sounds at different pitches.
These tests must be conducted without the use of hearing aids so that the VA can accurately measure your natural hearing ability.
How Hearing Loss Tests are Calculated
The VA uses the average result from your Pure Tone Threshold Test in each ear to see how severe your hearing loss is, following the rules in 38 CFR § 4.85 – Evaluation of Hearing Impairment, which explains how hearing tests and rating tables decide your VA rating.
Table VI

Table VI helps determine your level of hearing loss by combining your Maryland CNC score and your Pure Tone Threshold Average (PTA).
- The left column of Table VI shows your speech discrimination score (from 92–100% down to 0–34%).
- The top row displays your PTA results (ranging from 0–41 to 98+).
- The Roman numeral rating (I to XI) that represents your hearing level appears where your two scores intersect.
For example, if your Pure Tone Threshold Average is 56 and your Speech Discrimination score is 77%, your hearing level for that ear would be IV. Then, you repeat the process for your other ear.
Table VIA
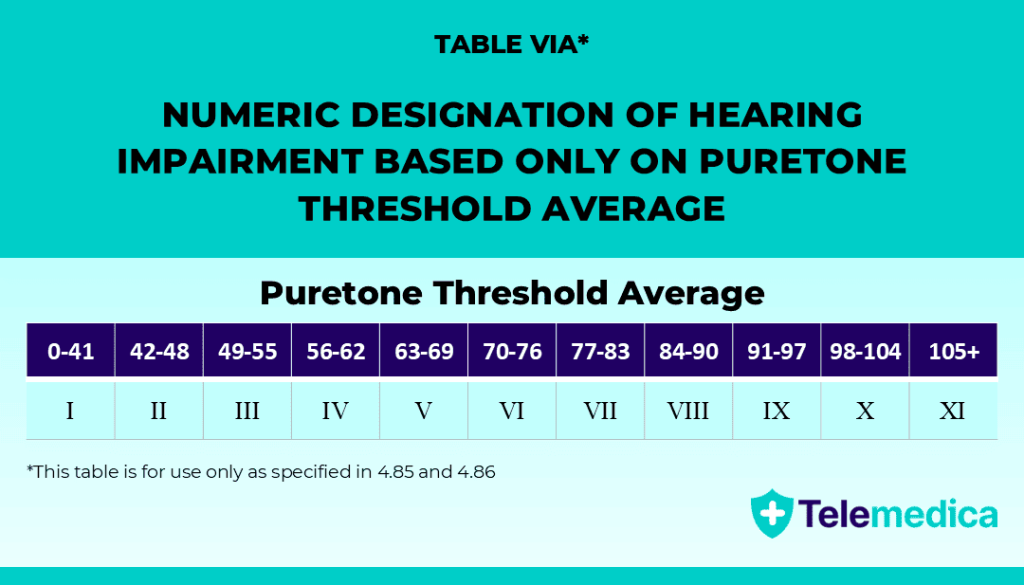
If language barriers, inconsistent results, or other issues prevent the use of the speech-discrimination test, the VA applies Table VIa instead.
This table assigns a Roman numeral based only on your average pure tone hearing score.
Table VII
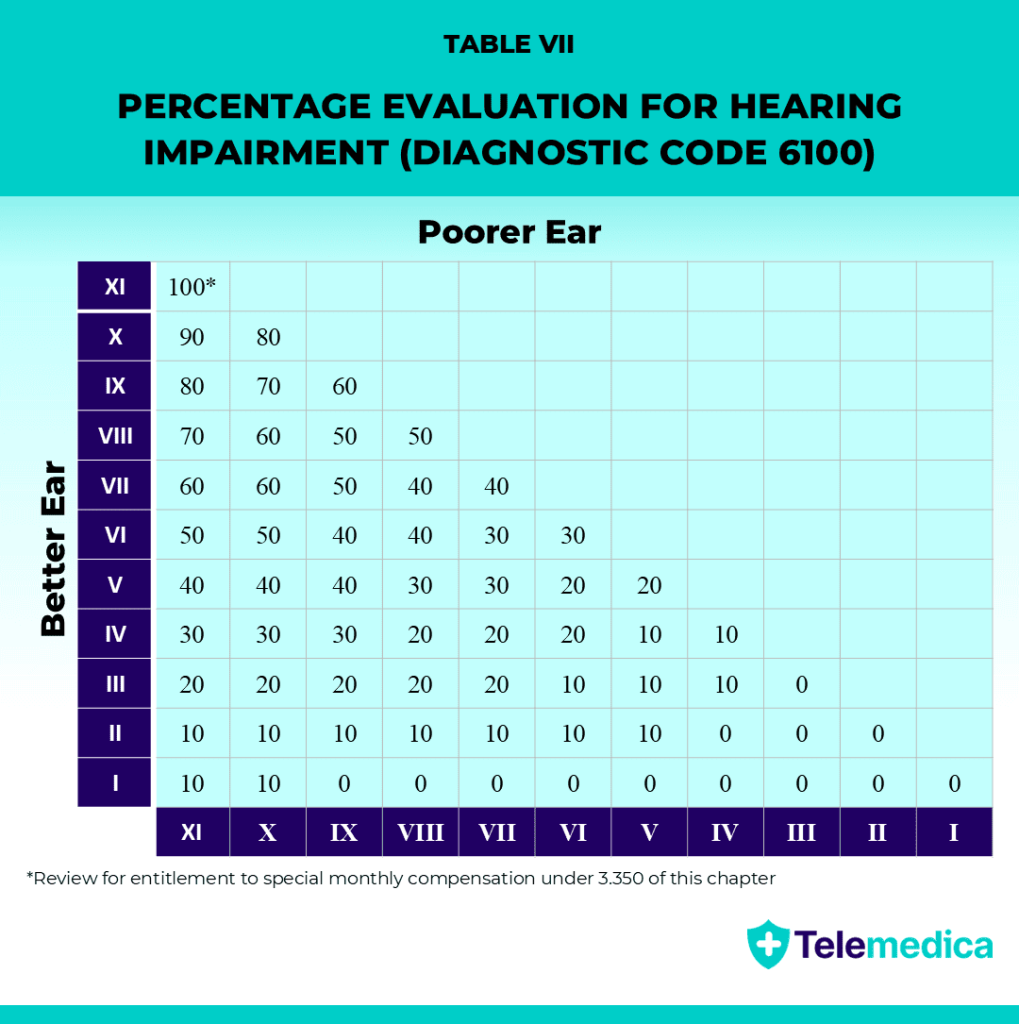
Once each ear has a Roman numeral, the VA uses Table VII to calculate your final VA hearing loss rating (0%–100%).
- The rows show the ear with better hearing.
- The columns show the ear with poorer hearing.
You can find your final disability percentage where those two numbers meet on the chart.
Example: If your poorer-hearing ear is assigned a VI and your better-hearing ear is assigned a VII, you will receive a final VA hearing loss rating of 30%.
Proving Service Connection for Hearing Loss
Direct Service Connection
Direct service connection means your disability was directly caused or aggravated by an event, injury, or illness that occurred while you were on active military duty.
To qualify for a direct service connection for hearing loss, you must provide evidence of the following:
- A current medical diagnosis
- An in-service event, injury, aggravation, or illness
- A medical nexus (link) between your current diagnosis and the in-service event, injury, aggravation, or illness
Secondary Service Connection
Secondary service connection applies when your hearing loss is caused or worsened by another service-connected condition.
Although this is less common, you can still qualify if medical evidence links the two, since the VA usually rates hearing loss as a direct condition.
A strong nexus letter from a licensed provider is essential to prove the connection.
To prove hearing loss as a secondary condition, you’ll need:
- A current medical diagnosis
- Medical evidence showing that your primary service-connected disability directly caused or aggravated your hearing loss
VA Disability Rating for Bilateral Hearing Loss
If your condition affects both ears, you may qualify for a VA disability rating for bilateral hearing loss.
The VA assigns a final disability rating by evaluating the severity of each ear separately. Since the VA considers both ears, this can lead to a higher overall rating than for unilateral hearing loss.
VA Ratings for Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
It’s possible to receive a VA rating for both hearing loss and tinnitus; however, the VA assigns separate ratings for each condition. Hearing loss is rated under DC 6100, while tinnitus is rated under DC 6260.
>> Learn more about Tinnitus VA Ratings and upcoming VA changes
VA Hearing Disability Rates 2026
Here are the 2026 VA hearing disability rates for a single veteran:
- 0%: Non-compensable ($0/month)
- 10%: $180/42/month
- 20%: $356.66/month
- 30%: $552.47/month
- 40%: $795.84/month
- 50%: $1,132.90/month
- 60%: $1,435.02/month
- 70%: $1,808.45/month
- 80%: $2,102.15/month
- 90%: $2,362.30/month
- 100%: $3,938.58/month
These amounts represent the monthly tax-free benefits a veteran without dependents can receive based on their VA disability rating. Veterans with dependents may receive higher monthly payments at ratings of 30% and above.
How to File a VA Claim for Hearing Loss
You can file a VA claim using VA Form 21-526EZ:
- By mail
- Via fax
- In person at a VA regional office
C&P Exam for Hearing Loss
If you file a VA claim for hearing loss, you’ll typically undergo a Compensation & Pension (C&P) exam.
The purpose of this exam is to confirm your current diagnosis, establish a service connection, and provide evidence needed to support your claim.
During the C&P exam, you can expect:
- A review of your medical history and a discussion of your symptoms
- Questions about your military noise exposure
- A physical examination of your ears
- Audiometric testing to measure your hearing sensitivity
- Completion of the Hearing Loss Disability Benefits Questionnaire (DBQ)
C&P Preparation Tips: Gather all relevant medical records, maintain a detailed symptom diary, and review the Hearing Loss DBQ to understand what the exam will assess.
Learn More: How Much Weight Does a C&P Exam Have?
Medical Evidence Wins Claims
Did you know that a lack of medical evidence is the #1 reason that VA disability claims are denied?
From nexus letters to IMOs and DBQs, we deliver the medical evidence you need to support your VA claim and set you up for success. Our service and support was built to serve veterans like you.
Book your 20-minute consultation today and get expert guidance that can put you on the fast track to winning your VA disability claim.
Final Thoughts
Securing a VA hearing loss rating can seem complicated because the VA relies on strict formulas and test results, rather than personal experiences.
The best way to strengthen your claim is to ensure you have high-quality audiology testing, clear evidence of service-related noise exposure, a current diagnosis, and a strong medical nexus linking your hearing loss to service.
Understanding how the VA evaluates hearing loss gives you a better chance of receiving the rating you rightfully deserve.
(FAQs) Frequently Asked Questions
What is the VA rating for hearing loss?
The VA bases a hearing loss rating on the results of two tests: the Pure Tone Audiometric Test and the Maryland CNC Test. The VA assigns a disability rating between 0% and 100% depending on how severe your hearing loss is in each ear.
What is the maximum VA rating for hearing loss?
The highest possible VA rating for hearing loss is 100%, indicating a profound loss of hearing in both ears that significantly impacts daily communication and functioning.
Is hearing loss a VA presumptive condition?
No. Hearing loss is not on the VA’s presumptive conditions list. That means the VA does not automatically assume your hearing loss was caused by military service, even if you had noise exposure.
Are there any VA secondary conditions to hearing loss?
Several conditions may be rated secondary to service-connected hearing loss. Common examples include tinnitus, anxiety or depression caused by communication difficulties, and possible balance disorders such as vertigo. Each condition must have medical evidence showing it was caused or aggravated by your service-connected hearing loss.
Is it hard to get VA disability for hearing loss?
It can be challenging. Even a 10% rating for hearing loss requires meeting strict VA testing criteria, but securing a strong nexus letter linking your hearing loss to service can significantly improve your chances of approval.
Can you get disability for hearing loss and tinnitus?
Yes. You can receive a VA disability rating for hearing loss and tinnitus; however, the VA assigns separate ratings for each condition. Hearing loss is rated under DC 6100, while tinnitus is rated under DC 6260.
What is the VA rating for hearing loss with hearing aids?
The VA rates your hearing loss based on how you hear without hearing aids. Even if you use hearing aids, the tests are conducted unaided, and the rating is determined based on those unaided results.
How much hearing loss does it take to qualify for disability?
To qualify for VA disability for hearing loss, your Maryland CNC and Pure Tone Threshold test results must meet the VA’s rating criteria. There is no specific decibel level required; only test scores high enough to produce a compensable rating under the VA’s tables.