How To Administer Semaglutide Injections A Step-by-Step Guide
By Telemedica
1/16/2025
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Obesity?
- What is Semaglutide?
- Recommended Semaglutide Dosage for Weight Loss
- Semaglutide Weight Loss Safety & Effectiveness
- How Do I Take Semaglutide?
- When is the Best Time to Take Semaglutide?
- Where’s the Best Place to Inject Semaglutide?
- How to Administer Semaglutide: Step-by-Step Guide
- How Do I Get Semaglutide?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that nearly 50 percent of Americans attempt to lose weight each year, and the World Health Organization (WHO) says that complications from obesity or being overweight kill at least 2.8 million people yearly in what the organization calls a “global epidemic.
These statistics follow the same trends for veterans. In 2014, the VA published a report estimating that approximately 78 percent of veterans were either overweight or obese. With obesity-related health issues on the rise, it’s no surprise that effective weight loss programs—including the use of Ozempic-like drugs such as semaglutide—continue to grow in popularity.
Learn how to administer semaglutide correctly (step-by-step), and learn more about the safety and effectiveness of semaglutide weight loss injections.
Key Takeaways
- The prevalence of overweight and obese adults in the U.S. continues to rise.
- A new Ozempic-like weight loss medication (i.e., GLP-1 receptor agonist) has been found safe and effective for obesity or overweight treatment.
- GLP-1 receptor drugs, such as semaglutide, are usually given via subcutaneous injection.

What is Obesity?
Obesity is a complex health issue caused by several factors, including genetics, diet, physical inactivity, and other causes, like medication use and exposure to various environmental factors.
The body mass index (BMI) is often used to diagnose obesity; this measure is reflected by a number denoting a person’s height and weight ratio. According to the CDC, a healthy BMI ranges from 18.5 to 24.9. If your BMI is 25 to 29.9, you are overweight; 30 or higher qualifies as obese.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a prescription weight loss medication classified as a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. GLP-1 drugs mimic the action of a hormone in the body–called GPL-1 hormone–that lowers blood sugar by increasing insulin secretion.
GLP-1 drugs were first developed to treat type 2 diabetes. Researchers initially discovered that these drugs helped control blood sugar, particularly with a healthy diet and exercise program. But it’s not necessary to be diabetic to take semaglutide; many doctors prescribe this weekly injectable weight-loss drug to overweight or obese individuals who are not diabetic for its weight-loss benefits.
Semaglutide’s popularity is gaining momentum as a growing body of medical research shows its many benefits.
Recommended Semaglutide Dosage for Weight Loss
Nondiabetics typically take a slightly higher dose of semaglutide for weight loss than those with type 2 diabetes.
Semaglutide is given via subcutaneous (i.e., under the skin) injections at an initial dose of 0.25 mg once a week for four weeks for weight loss. After four weeks your dosage will gradually increase until you reach the maintenance dose of 2.4 mg per week.
Semaglutide Benefits
The weight loss benefits of semaglutide are well known today. Semaglutide and other GLP-1 agonist medications help you lose weight by lowering your blood sugar, reducing food cravings, decreasing your appetite and inducing a sense of fullness after a meal; other benefits of semaglutide include:
- Increasing insulin sensitivity, which enhances the cells’ use of glucose blood (i.e., sugar)
- Lowering type 2 diabetes risk
- Lowering blood pressure
- Reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, diabetes and some cancers
- Improving cholesterol levels and reducing triglycerides (i.e., a type of fat that circulates in the blood contributing to arterial plaque build-up and stroke risks)
Semaglutide Side Effects
Common semaglutide side effects of semaglutide include swelling, redness, itching, or pain at the injection site. Other common side effects include:
- Fatigue, headache, and dizziness
- Disturbances of the digestive system, such as heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and bloating
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Stomach pain
On rare occasions, semaglutide injections can cause severe side effects, including allergic reactions. Signs of an allergic reaction include hoarseness, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the mouth, throat, or hands. If you experience allergic symptoms, seek immediate emergency medical attention.
Semaglutide Weight Loss Safety & Effectiveness
Semaglutide Safety
In a 2021 study, researchers examined the safety of injectable semaglutide. The study showed that the most common side effects were mild and temporary, including gastrointestinal (stomach and intestine) problems, like nausea and diarrhea. The study authors stated, “No major safety concerns have arisen to date.”
Semaglutide Effectiveness
Study reviews conducted in 2022 report that participants taking semaglutide lost between 5% and 20% of their body weight.
How Do I Take Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is usually prescribed via weekly subcutaneous (i.e., under the skin) injections.
If you are just starting your GLP-1 weight loss program, you may wonder how to inject semaglutide for weight loss.
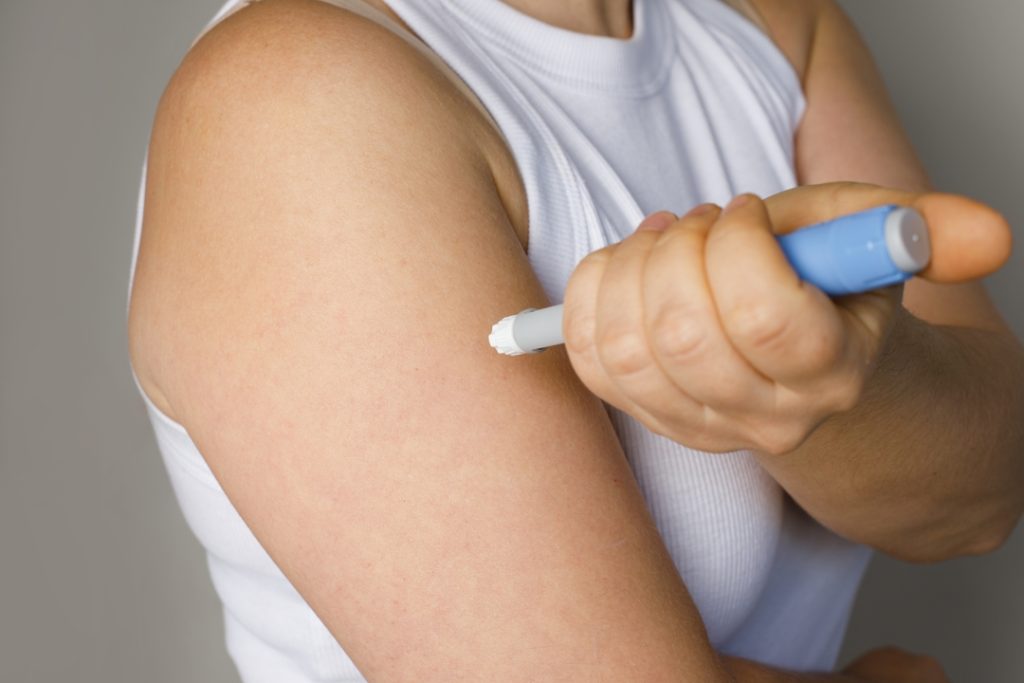
Semaglutide is administered subcutaneously (under the skin) once a week on the same day of the week. The medicine is injected subcutaneously (under the skin), rotating the injection site each time. It can be given to your stomach, upper arms, thighs, or back.
It may be difficult to self-administer your medication on some sites, so you may want to get help from a friend or family member before using the upper arms or back.
By injecting semaglutide in different parts of your body each time you give yourself an injection, you increase your chances of maintaining a steady amount of medication absorption.
When is the Best Time to Take Semaglutide?
You can take the medication any day of the week, preferably around the same time each day.
You can change the day of the week that you take your semaglutide as long as it has been 2 or more days (48 or more hours) since you injected your last shot.
Where’s the Best Place to Inject Semaglutide?
The best place to inject Semaglutide is in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm, being sure to rotate the injection sites every week.
How to Administer Semaglutide: Step-by-Step Guide
Semaglutide comes in a multi-dose vial; it can be self-administered via injection in the abdomen or thighs. If someone else helps with your injection, other sites can be used, such as the upper arms or back.
Make sure you understand how to administer semaglutide properly before injecting it.
There are several steps involved in preparing and administering semaglutide injections.
Gather Your Supplies
First, gather your supplies, including:
- Your semaglutide vial
- A new insulin syringe with a clean needle
- Alcohol pads, a Band-Aid
- An FDA-approved sharps container
Step #1. Remove the semaglutide vial containing the medication from your refrigerator.
Step #2. Ensure the vial is labeled correctly with the name of your medication (i.e., semaglutide) and the correct dosage prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Step #3. Examine the medication to ensure its thoroughly thawed, colorless, or slightly yellow-tinged, and not cloudy (a cloudy color could indicate the medication is expired).
Step #4. Check the expiration date.
Step #5. Wash your hands thoroughly with hot water and soap.
Prepare the Syringe
Step#6. Remove the cap from the semaglutide vial and clean the rubber stopper with a new alcohol pad
Step #7. Draw air the amount of air that is equal to the semaglutide dose you are going to inject into the syringe.
Step #8. Remove the cap from the needle and dispose of it in the regular garbage container, then insert the needle into the rubber stopper of the semaglutide vial and inject—by pushing the syringe all the way down—all the air you’ve drawn up in the syringe plunger. Note., injecting air helps equalize the pressure in the bottle. Don’t remove the needle.
Step #9. With the needle still in the vial, turn the medication bottle upside down making sure the needle is submerged in the fluid; now draw up the desired amount of semaglutide medication into the insulin syringe.
Step #10. Slowly, gently push the syringe plunger down to remove any air bubbles, tapping the syringe with your fingers to help the bubbles rise to the top.
Administer the Semaglutide Injection
Step #11. Select an injection site; if you have questions, talk to your healthcare provider about which site is best for you.
Step #12. Wipe the injection site with alcohol and allow it to air dry.
Pinch the skin at the injection site.
Step #13. Place the needle at a 45 to 90-degree angle into the skin using the syringe like a dart.
Step #14. Release the pinched skin once the needle is in, then push the plunger to inject the semaglutide medication.
Step#15. Once all the medication is injected pull the needle out, then discard the syringe and needle together in an FDA sharps container; never dispose of used needles in a household trash container.
How Do I Get Semaglutide?
Discover how Telemedica’s new prescription weight management program can help you lose weight effectively – with providers specializing in treating veterans.
We offer weight management telehealth services for veterans and non-veterans.
Upon approval, a treatment specialist will contact you and enroll you in our program. The semaglutide bundled weight loss cost includes a doctor’s consultation, your semaglutide medication, and all the medical equipment necessary for administering the shots.
Getting your prescription weight loss medication shipped to your door only takes a few simple steps.
First, complete our online medical form; next, consult with one of our online Telemedica specialists, and finally, wait for your prescription to be conveniently shipped to your door from one of our pharmacy partners.